
About Corrugated
What is Corrugated?
Corrugated fiberboard or "combined board" has two main components: the liner and the medium.
Corrugated fiberboard or "combined board" has two main components: the liner and the medium. Both are made of a special kind of heavy paper called containerboard. Linerboard is the flat material, typically on the outer surfaces of the board but also on the inside for some structures, that adheres to the medium. Medium is the paper that is formed into arches or flutes on the single facer and glued between the linerboard facings.
Flutes
Architects have known for thousands of years that an arch with the proper curve is the strongest way to span a given space. The inventors of corrugated fiberboard applied this same principle to paper when they put arches in the corrugated medium. These arches are known as flutes and, when anchored to the linerboard with an adhesive, they resist bending and pressure from all directions.
When a piece of combined board is placed on its end, the arches form rigid columns, capable of supporting a great deal of weight. The flutes act to keep the linerboard sheets separated, maximizing the bending rigidity of the board. When pressure is applied to the side of the board, the space in between the flutes acts as a cushion to protect the container's contents. The flutes also serve as an insulator, providing some product protection from sudden temperature changes. At the same time, the vertical linerboard provides additional strength and protects the flutes from damage.
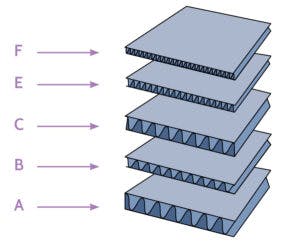
Flutes come in several basic designations. Flutes with the same designation have similar size, but may have various flute profiles and number of flutes per foot within a given designation:
- A flute was the original flute profile for corrugated board. It has about 33 flutes per foot.
- B flute was then developed for canned goods that were self-supporting, and so did not require boxes that supported much load. It has about 47 flutes per foot.
- C flute was next developed as an all-purpose flute, and it has about 38 flutes per foot.
- E flute was the next successful flute profile, and it has about 90 flutes per foot.
- F flute was developed for small folding carton type boxes. It has about 125 flutes per foot.
In recent years not only has there been a proliferation of flute profiles, but there has been increase in the variation in flute characteristic measurements for any given flute profile. Flute profiles will vary, sometimes significantly, because the corrugator rolls are manufactured to address a variety of aspects (such as speed, paperboard characteristics, economies, etc.).
Combined Board
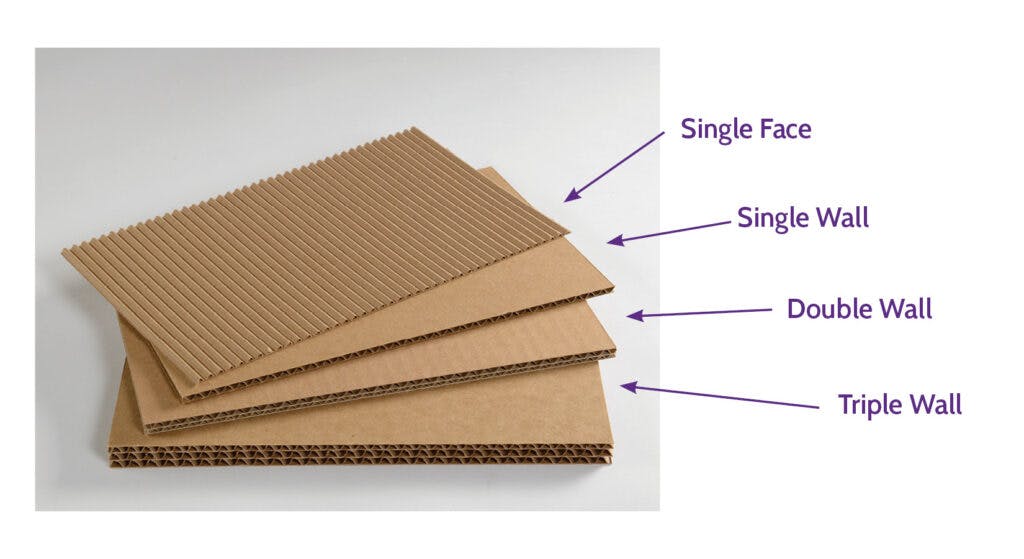
The below illustration demonstrates four basic types of combined board that are most commonly created from linerboard and medium using the variety of flute structures:
- Single Face: One corrugated medium is glued to one flat sheet of linerboard.
- Single Wall: The corrugated medium is glued between two sheets of linerboard. Also known as Double Face.
- Double Wall: Three sheets of linerboard with two mediums in between.
- Triple Wall: Four sheets of linerboard with three mediums in between.
Generally, larger flute profiles deliver greater cushioning and vertical compression strength, while smaller flute profiles provide enhanced graphics capabilities. Smaller flutes such as E and F also provide enhanced structural capabilities for primary (retail) packaging compared to paperboard (folding cartons). There is a good deal of variance across the industry in the range of flute sizes based upon the container characteristics that are desired for each application, as well.
Box Styles
Boxes can be used to ship everything from apples to washing machines. By changing the design of a box, combining layers of corrugated or adding interior packaging, a corrugated box can be manufactured to efficiently ship and store almost any product.
Many standard box styles can be identified in three ways: by a descriptive name, by an acronym based on that name, or by an international code number. The numerical code system, known as the International Fibreboard Case Code, was developed by the European Federation of Corrugated Board Manufacturers (FEFCO) in collaboration with the European Solid Board Organisation (ESBO) to avoid confusion when communicating in different languages.
Below are some common box style categories and designs. Keep in mind there are many other standard styles from which to choose. In addition, corrugated boxes can be custom designed to meet the specific needs of any box user. A manufacturer's representative will have more information about additional box style options.
Slotted Boxes:
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 02 Series
Telescope Boxes:
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 03 Series
Folders:
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 04 Series
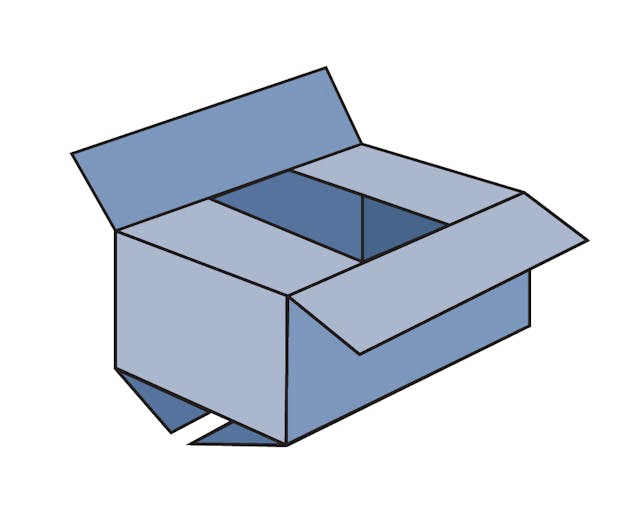
0201 Regular Slotted Container (RSC)
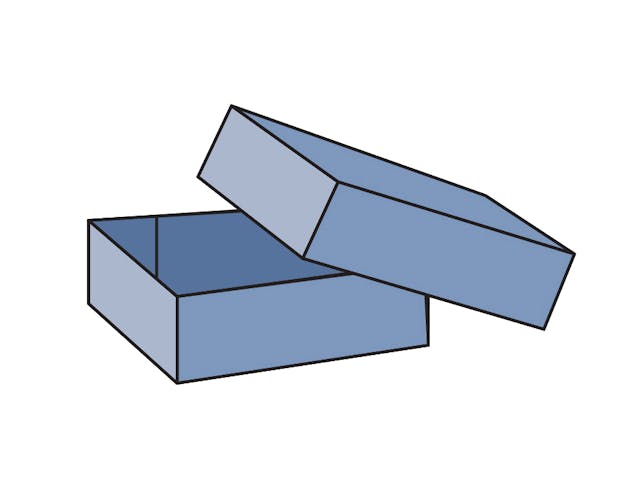
0301 Full Telescope Design Style Container (FTD)
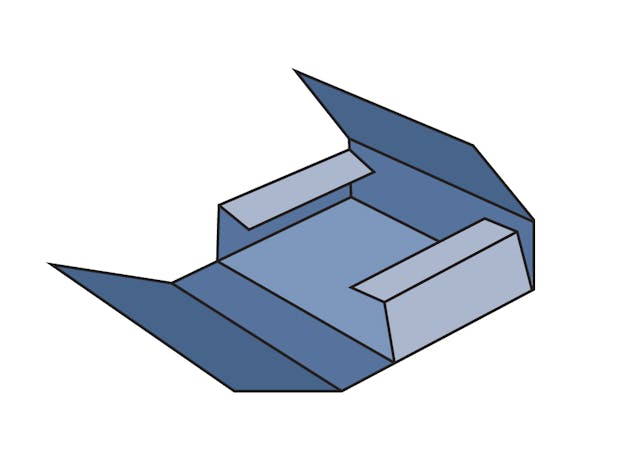
0401 One Piece Folder (OPF)
Rigid Boxes (Bliss Boxes):
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 06 Series
Self Erecting Boxes:
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 07 Series
Interior Forms:
International Fibreboard
Case Code: 09 Series
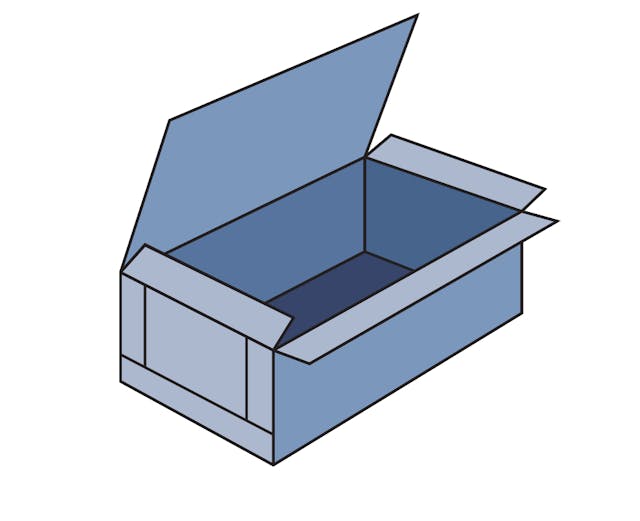
0601A Bliss Style Container with End Flaps
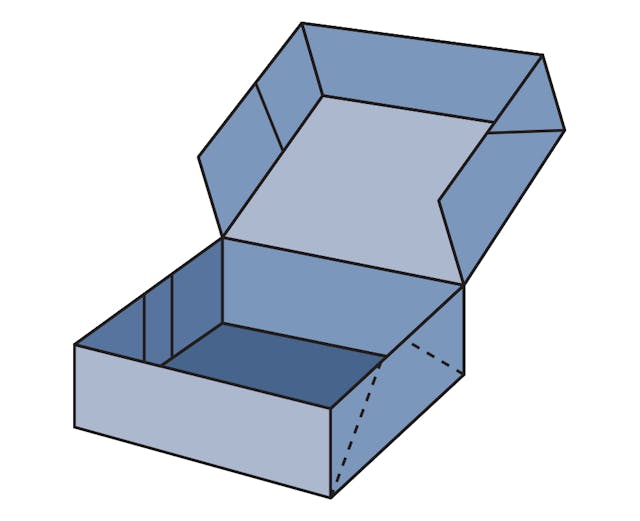
0760 Self Erecting Six Corner Tray

0904 Tube